

Isolated protoplasts are also exploited in numerous miscellaneous studies involving membrane function, cell structure, synthesis of pharmaceutical products, and toxicological assessments. Uptake of isolated DNA into protoplasts provides the basis for transient and stable nuclear transformation, and also organelle transformation to generate transplastomic plants. In the context of plant genetic manipulation, somatic hybridisation by protoplast fusion enables nuclear and cytoplasmic genomes to be combined, fully or partially, at the interspecific and intergeneric levels to circumvent naturally occurring sexual incompatibility barriers. Nevertheless, isolated protoplasts are unique to a range of experimental procedures. However, despite at least four decades of concerted effort and technology transfer between laboratories worldwide, many species still remain recalcitrant in culture. Importantly, novel approaches to maximise the efficiency of protoplast-to-plant systems include techniques already well established for animal and microbial cells, such as electrostimulation and exposure of protoplasts to surfactants and respiratory gas carriers, especially perfluorochemicals and hemoglobin. Protoplasts from Arabidopsis plants were prepared as described previously (Lee et al., 2008). Several parameters, particularly the source tissue, culture medium, and environmental factors, influence the ability of protoplasts and protoplast-derived cells to express their totipotency and to develop into fertile plants. Reliable procedures are available to isolate and culture protoplasts from a range of plants, including both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous crops. Major advances in genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics have stimulated renewed interest in these osmotically fragile wall-less cells. in the Non-Photosynthetic Parasitic Plant, Orobanche minor Sm. Using these novel insights and four-dimensional time-lapse imaging data, we propose a model that can explain the mechanism by which changes in microtubule dynamic instability drive the dramatic rearrangements of microtubules during preprophase band and spindle formation in plant cells.Plant protoplasts (“naked” cells) provide a unique single cell system to underpin several aspects of modern biotechnology. Strikingly, during preprophase band formation, the growth rate and catastrophe frequency of plant microtubules double, whereas the shrinkage rate and rescue frequency remain unchanged, making microtubules shorter and more dynamic. The interphase plant microtubules grow at 5 μm/min, shrink at 20 μm/min, and display catastrophe and rescue frequencies of 0.02 and 0.08 events/s, respectively, exhibiting faster turnover than their mammalian counterparts. Using plus-end labeling, we observed dynamic instability in different microtubular conformations in live plant cells.
Add 10µl DNA (1020µg of plasmid DNA of 510 kb in size) to 1.5ml tube 2.
96 well plate 4.0 Prescribed Actions DNA-PEGcalcium transfection (Less than 1 h for 20 samples) 1.

#PLANT PROTOPLAST TRANSFECTION MIDIKIT PLUS#
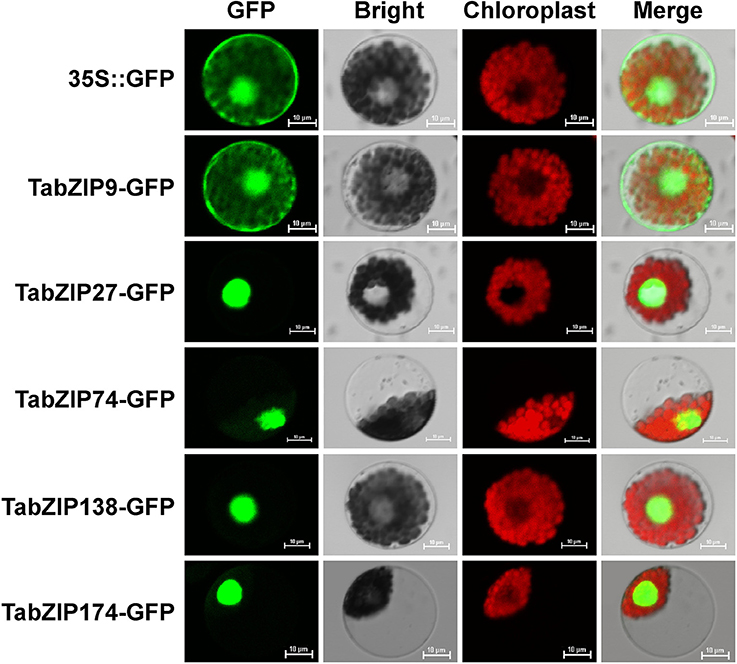
Here, we describe the use of mammalian yellow fluorescent protein-tagged CLIP170 to visualize the dynamic plus ends of plant microtubules in transfected cowpea protoplasts and in stably transformed and dividing tobacco Bright Yellow 2 cells. ARC COE for Plant Success in Nature and Agriculture: Protoplast Transfection LSOP26 Version: 1.1 Effective Date: of 3 7. Maintain healthy plant growth and avoid poor plant growth are critical for protoplasts isolation. At the onset of mitosis, plant cells form a microtubular preprophase band that defines the plane of cell division, but the mechanism of its formation remains a mystery. It is critical to use young plants (3- to 4-week-old) as older plants seem more difficult to digest and result in more cell debris and lower yields of protoplasts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
